looping statements in C ( while, do while , for)
Types of Loops in C
Depending upon the position of a control statement in a program, looping in C is classified into two types:
2. Exit controlled loop
In an entry control loop in C, a condition is checked before executing the body of a loop. It is also called as a pre-checking loop.
In an exit controlled loop, a condition is checked after executing the body of a loop. It is also called as a post-checking loop.
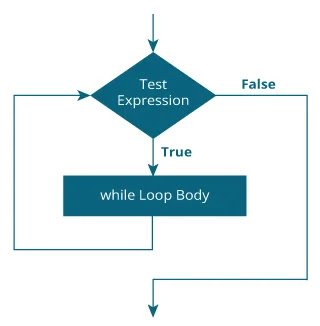
while loop ( entry controlled)
do...while loop ( exit controlled)
for loop ( entry controlled)for Loop
The syntax of a while loop is:
while (testExpression)
{
//codes
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
long long factorial;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d",&number);
factorial= 1;
//loop terminates when number is less than or equal to 0
while(number > 0)
{
factorial*= number;
--number;
}
printf("Factorial=%lld", factorial);
return 0;
}
Syntax: do...while loop
do
{
// codes
}
while (testExpression);
// Program to add numbers until user enters zero
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double number, sum = 0;
//loop body is executed at least once
do
{
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf",&number);
sum+= number;
}
while(number!= 0.0);
printf("Sum= %.2lf",sum);
return 0;
}
| while | do-while |
|---|---|
| Condition is checked first then statement(s) is executed. | Statement(s) is executed atleast once, thereafter condition is checked. |
| It might occur statement(s) is executed zero times, If condition is false. | At least once the statement(s) is executed. |
| No semicolon at the end of while. while(condition) | Semicolon at the end of while. while(condition); |
| If there is a single statement, brackets are not required. | Brackets are always required. |
| Variable in condition is initialized before the execution of loop. | variable may be initialized before or within the loop. |
| while loop is entry controlled loop. | do-while loop is exit controlled loop. |
| while(condition) { statement(s); } | do { statement(s); } while(condition); |
for loop
It is an entry controlled looping statement
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement)
{
// statements
}
Then, the test expression is evaluated. If the test expression is false (0), for loop is terminated. But if the test expression is true (nonzero), statements inside the body of for loop is executed and the update expression is updated.
This process repeats until the test expression is false.
The for loop is commonly used when the number of iterations is known.
// Program to calculate the sum of first n natural numbers
// Positive integers 1,2,3...n are known as natural numbers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num, count, sum = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
// for loop terminates when n is less than count
for(count = 1; count <= num; ++count)
{
sum+= count;
}
printf("Sum= %d", sum);
return 0;
}
- Selection of a loop is always a tough task for a programmer, to select a loop do the following steps:
- Analyze the problem and check whether it requires a pre-test or a post-test loop.
- If pre-test is required, use a while or for a loop.
- If post-test is required, use a do-while loop.
Summary
- Looping is one of the key concepts on any programming language.
- A block of loop control statements in C are executed for number of times until the condition becomes false.
- Loops are of 2 types: entry-controlled and exit-controlled.
- 'C' programming provides us 1) while 2) do-while and 3) for loop.
- For and while loop C programming are entry-controlled loops.
- Do-while is an exit-controlled loop.
Sample programs ( all university questions)
Print factors of a number
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int n,i;
printf("Enter the number...\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Factors of the number\n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(n%i==0)
printf("%d\n",i);
}
Note: an efficient way is to go up to n/2
Check whether the given number is prime or not
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
main()
{
int n,flag=1,i;
printf("enter a number n >1 for primality test\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++)
if(n%i==0)
{ flag=0;break;}
if(flag==1)
printf("%d is prime \n",n);
else
printf("%d is not prime \n",n);
}
Print Fibonacci Series up to 100
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int a=0,b=1,c=1;
while(c<100)
{
printf("%d, ", c);
c = a+b;
a= b;
b=c;
}
printf("\n");
}
Program to reverse a number
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int n, rev = 0, digit;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n != 0) {
digit= n % 10;
rev = rev * 10 + digit;
n /= 10;
}
printf("Reversed number = %d\n", rev);
}
printing the sin series x^1/1!-x^3/3!+x^5/5!.......x^20/20!
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int i,sign=1;
for(i=1;i<=20;i+=2)
{
printf("x^%d/%d!",i,i);
sign=-sign;
if(sign==-1)
printf("-");
else
printf("+");
}
}
Check for perfect number ( Eg: 6,28,496 etc..)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int n,i,s=0;
printf("Enter the number\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n/2;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
s=s+i;
}
if(s==n)
printf("%d is a perfect number \n",n);
else
printf("%d is a not a perfect number \n",n);
}
Write a C program to find the sum of first and last digit of a number.
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int n, fdig,ldig;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
ldig=n%10;
while (n != 0) {
fdig=n%10;
n /= 10;
}
printf("Sum of first and last digit = %d\n", fdig+ldig);
}
Write C program to convert the given decimal number into binary number.( university question)
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int i,n,bit,bin=0,place=1;
printf("Enter the number:");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n!=0)
{
bit=n%2;
bin=bin+bit*place;
n=n/2;
place=place*10;
}
printf("Binary=%d\n",bin);
}
2)Print the odd numbers between 0 and 50 in the reverse order ( use while)
3)Print the series 5,10,15,….,100 (using for loop)
4)Generate the series 1, 2, 4 ,7, 11 ,16....n ( use while...read n)
5)Generate the Fibonacci series 0 1 1 2 3 5 8…..n ( use do while..read n)
6)Find the factorial of a number ( use for statement do not use built in factorial() function)
7)Print the powers of a number upto 10th power. ( Eg: if n=2 then the program should print 2^0, 2^1, 2^2,2^3,…..,2^10 use for loop)
8)Print the multiplication table of a given number. ( use while)
9)Print the numbers from 1 to 10 and their natural logarithms as a table ( use for)
10)Find the sum of the digits of a number.( use while-university question)
11)Check whether the given 3 digit number is an Armstrong number. (use do while Eg:153,370,371,407) ( uq)
12)Find the factors of a number ( use for)
13)Check whether the given number is prime or not ( use for)
14) Find the GCD or HCF of two numbers ( use Euclid algorithm and while loop)
15) Reverse a number (use while)
16)Find the numbers between 10 and 1000 that are divisible by 13 but not divisible by 3
( use for)
17)Find the sum of series 1-x^2/2+x^4/4-x^6/6........x^n/n ( use while)
18)Check whether the given number is a Krishnamurti number( Krishnamurti Number: It is a number which is equal to the sum of the factorials of all its digits.
For example : 145 = 1! + 4! + 5! = 1 + 24 + 120 = 145)
19)Read N numbers and find the biggest and smallest. ( university question)
20)Read N numbers and find the sum of all odd and even numbers separately.(university question)
21)Count the number of digits in a number.(university question)
22)Write a C program to input a list of n numbers. Calculate and display the sum of cubes of each value in the list.(university question)
23)Write a C program to count the number of zeros and negative terms in a given set of n numbers.
24)Write a C program to input a list of n numbers. calculate and display the average of numbers. Also display the cube of each value in the list.( university question)
25)read mark of n students and print the average mark.Also print the number of students who scored more than 80% mark (mark out of 50)
26)Find the sum s=1+2/3!+3/5!+4/7!... n
27)Write a C program to evaluate the series x-x^3/3!+x^5/5!-x^7/7!....n(uq)
29)Print the pattern 101010....using for loop(uq)






Comments
Post a Comment